Antifungal Drugs
Antifungal drugs are medications used to treat fungal infections, which can affect various parts of the body including the skin, nails, hair, and internal organs. These drugs work by targeting and inhibiting the growth of fungi, thereby treating or preventing the spread of infection. Antifungal drugs can be classified based on their chemical structure, mechanism of action, and the type of fungal infections they treat.
Uses of Antifungals
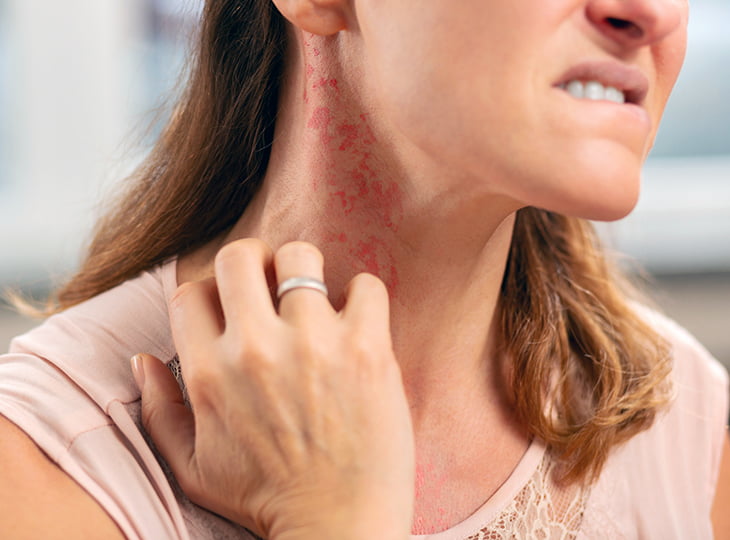
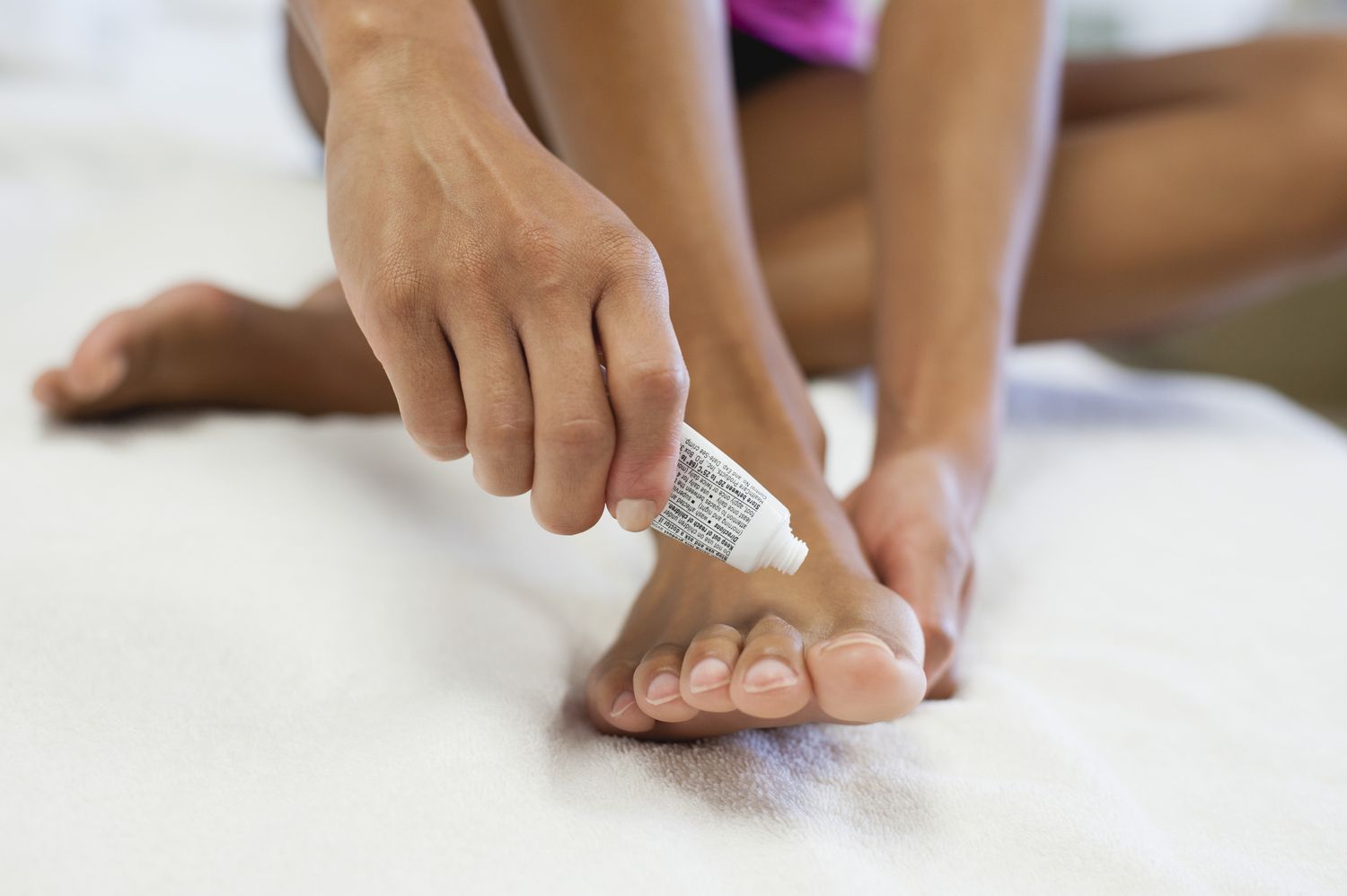
Superficial Fungal Infections: Skin, nails, hair (e.g., ringworm, athlete’s foot, jock itch, nail fungus).
Mucosal Infections: Oral thrush, vaginal yeast infections.
Systemic Fungal Infections: Fungal infections affecting internal organs, such as the lungs (aspergillosis), bloodstream (candidemia), or brain (cryptococcal meningitis).
Side Effects
Azoles: Can cause liver toxicity, hormonal imbalances, and drug interactions.
Polyenes: Amphotericin B can cause kidney damage, electrolyte imbalances, and infusion-related reactions.
Echinocandins: Generally well-tolerated, but may cause liver function changes.
Allylamines: Terbinafine can cause gastrointestinal disturbances and, rarely, liver toxicity.

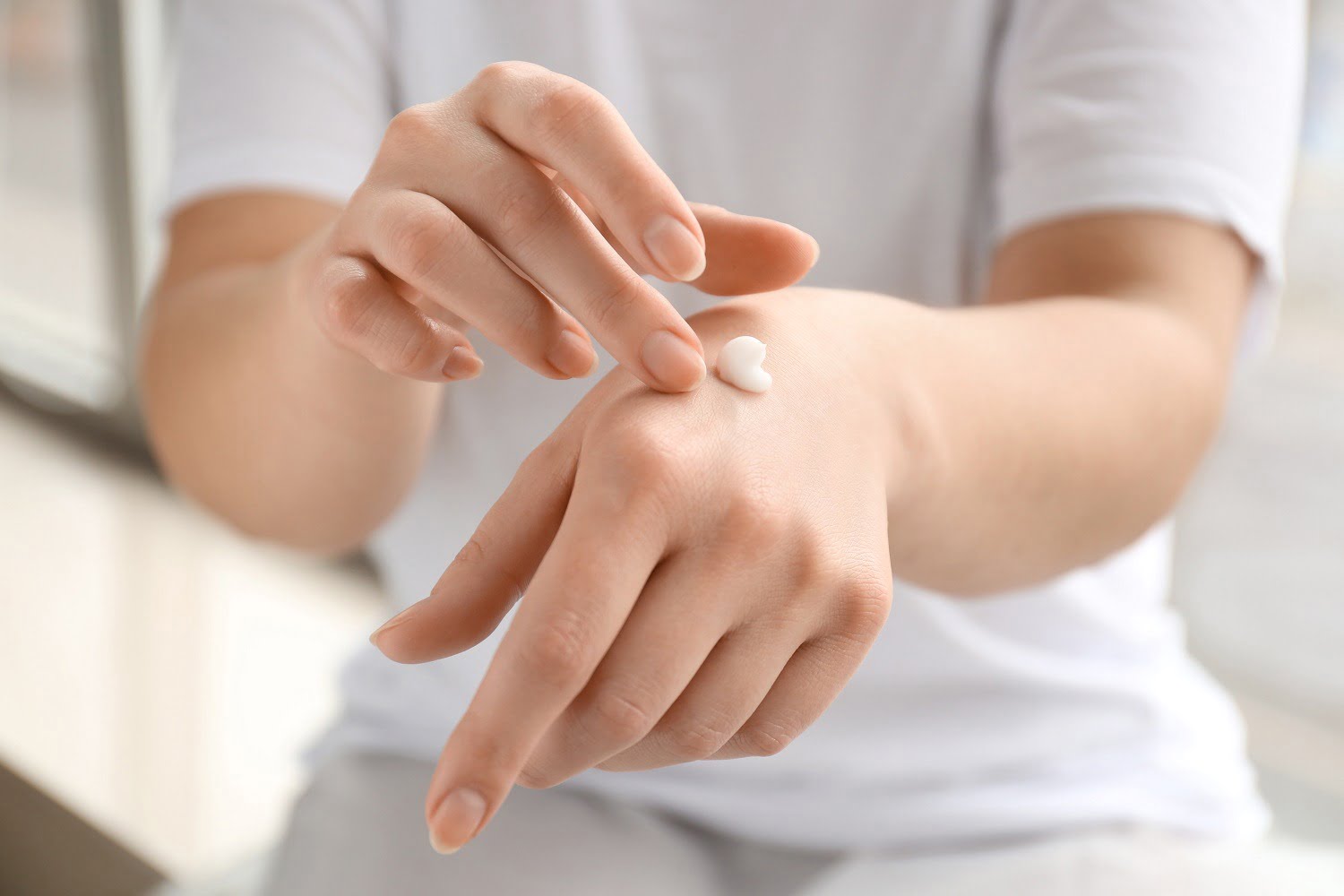

Azoles
Azoles work by inhibiting an enzyme called lanosterol 14α-demethylase, which is essential for the synthesis of ergosterol, a key component of fungal cell membranes.
Polyenes
Polyenes bind to ergosterol in the fungal cell membrane, creating pores that allow essential ions and molecules to leak out, leading to cell death.
Echinocandins
Echinocandins inhibit the synthesis of β-glucan, an essential component of the fungal cell wall, leading to cell wall weakening and eventual fungal cell death.
Download Brochure
Get access to our comprehensive guide to our Antifungal drug catalogue.
Our Range of Antifungal Drugs
Mycostat Tablet
Mycocort Cream
Gyno-Mycolex
Mycolex Range
Battle Fungal Infections The Effective Way
Bring happiness back to your life with our range of Antifungal products.
