Antidiabetic Drugs

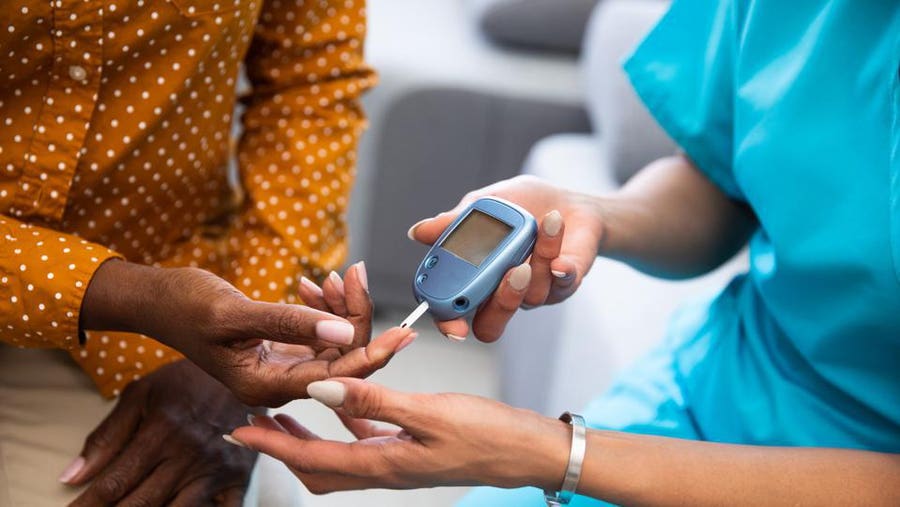
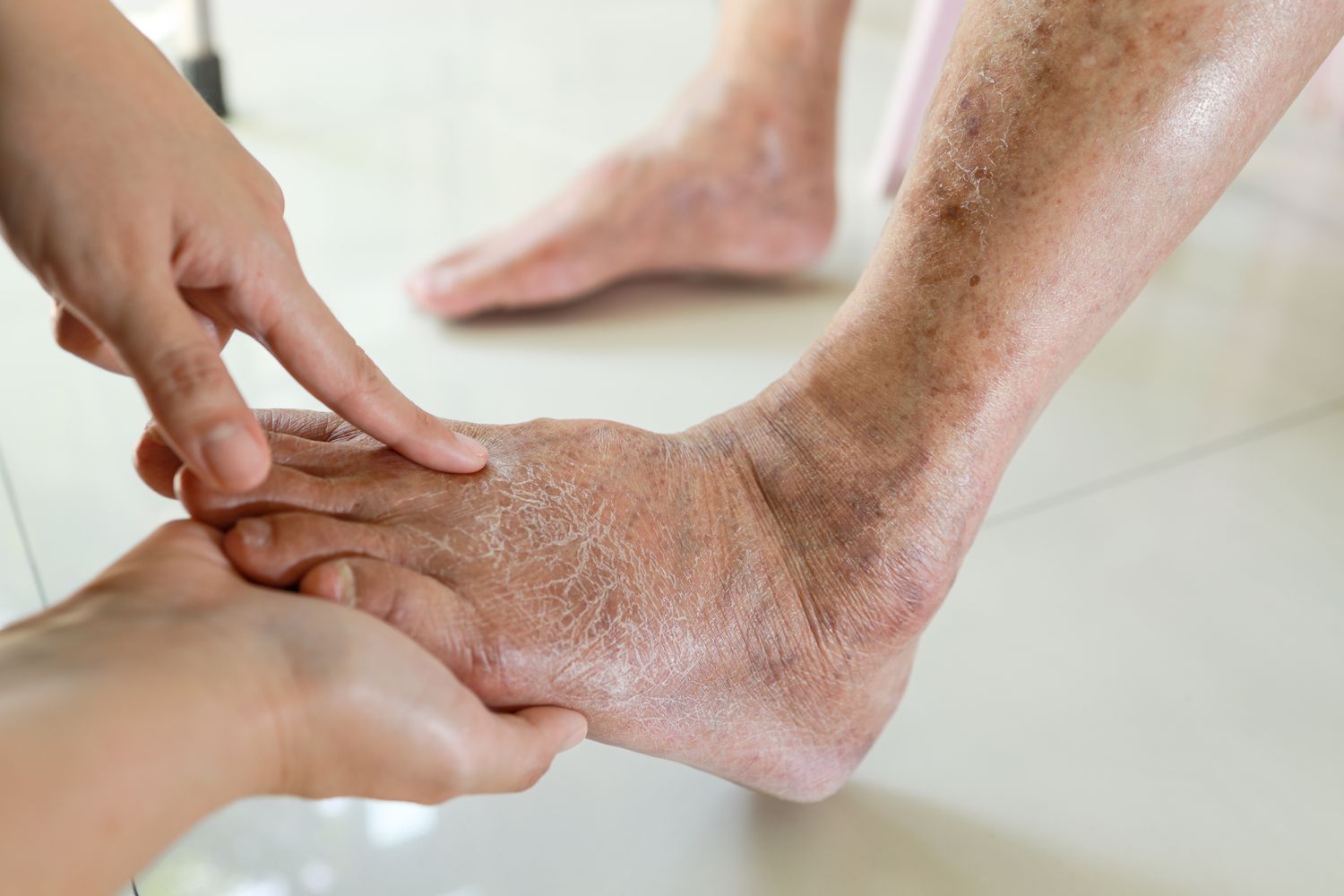
Antidiabetic drugs are medications used to treat diabetes mellitus, a condition characterized by high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia) due to the body’s inability to produce or effectively use insulin. These drugs help control blood glucose levels and are critical in managing both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes.
Uses of Antidiabetic Drugs
Type 1 Diabetes: Typically requires insulin therapy, as the body cannot produce insulin.
Type 2 Diabetes: Often managed with oral medications like metformin, sulfonylureas, or newer agents like DPP-4 inhibitors and SGLT2 inhibitors. Insulin may also be used if other medications do not adequately control blood glucose levels.
Gestational Diabetes: Can be managed with diet, exercise, and insulin if necessary.
Side Effects
- Insulin: Risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), weight gain, and injection site reactions.
- Metformin: Gastrointestinal issues such as nausea, diarrhea, and a rare risk of lactic acidosis.
- Sulfonylureas: Risk of hypoglycemia and weight gain.
- TZDs: Risk of weight gain, fluid retention, heart failure, and bone fractures.
- DPP-4 Inhibitors: Generally well-tolerated, but may cause upper respiratory tract infections.
- GLP-1 Agonists: Risk of gastrointestinal symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and potential weight loss.
- SGLT2 Inhibitors: Risk of urinary tract infections, genital infections, and dehydration.


Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors
DPP-4 inhibitors block the enzyme DPP-4, which degrades incretins (hormones that increase insulin secretion in response to meals).
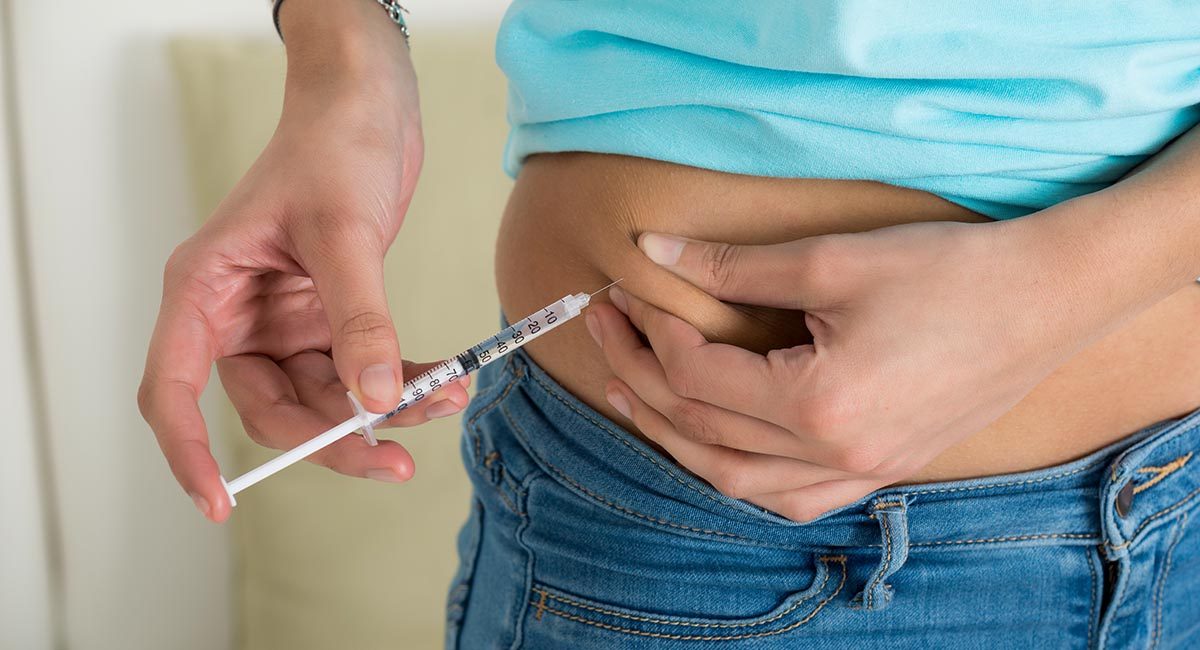
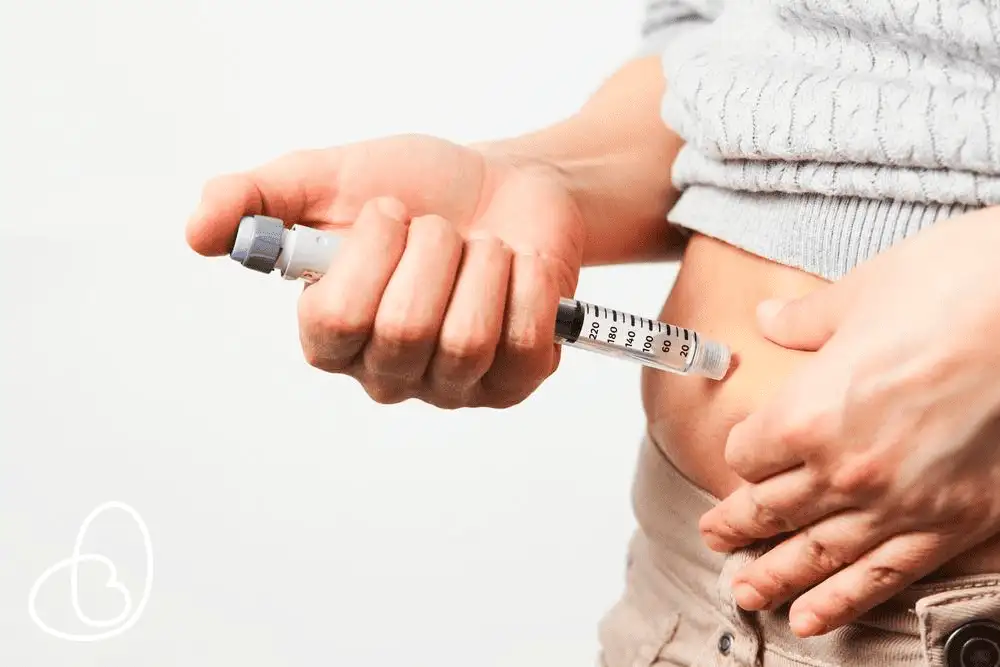
Insulin
Insulin is a hormone that helps cells absorb glucose from the blood. It lowers blood sugar levels by promoting the uptake of glucose into cells, storing glucose as glycogen in the liver, and reducing the production of glucose by the liver.
Sulfonylureas
Sulfonylureas stimulate the pancreas to release more insulin by binding to and closing potassium channels on beta cells, leading to insulin secretion.
Download Brochure
Get access to our comprehensive guide to our Cardiovascular drug catalogue.
Our Range of Antidiabetic Drugs

Glimpride

Lexformin
Battle Diabetes The Effective Way
Bring happiness back to your life with our range of Antidiabetic products.
